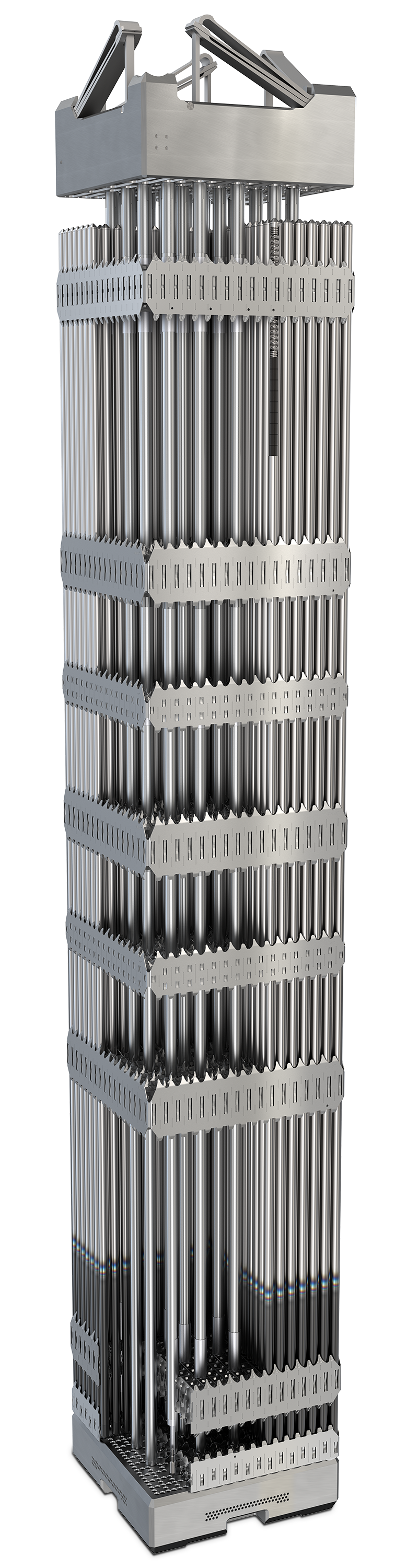
Compatible products and technologies, designed to provide enhanced performance and bring measurable benefits to operating utilities in pursuit of increased margins, more demanding fuel cycles, and improved economics. These technologies can be deployed individually or combined across Westinghouse’s multiple fuel product arrays.
Top of Assembly
Click on one of the features below to learn more about their benefits.
Middle of Assembly
Click on one of the features below to learn more about their benefits.
Bottom of Assembly
Click on one of the features below to learn more about their benefits.
Mounted on the top plate of the WIN Top Nozzle and are designed to provide the desired spring constant, deflection range, and net holddown forces for the assembly under flow conditions.
Functions as the upper structural element of the fuel assembly and utilizes the removable top nozzle (RTN) feature to facilitate fuel rod examination and replacement.
Composed of straps, which are brazed together to form the grid structure and maintain contact force through end of life. The top grid has integral grid strap springs with a low force to mitigate fuel rod bow.
A UO2 pellet doped with chromia (Cr2O3) and alumina (Al2O3) that facilitate diffusion during sintering, resulting in a higher density and an enlarged grain size which enhances the accident tolerance of our fuel design.
Specifically designed for increased core operating fuel duties and high burnup applications with improved corrosion resistance, lower hydrogen pick-up, and lower creep and growth.
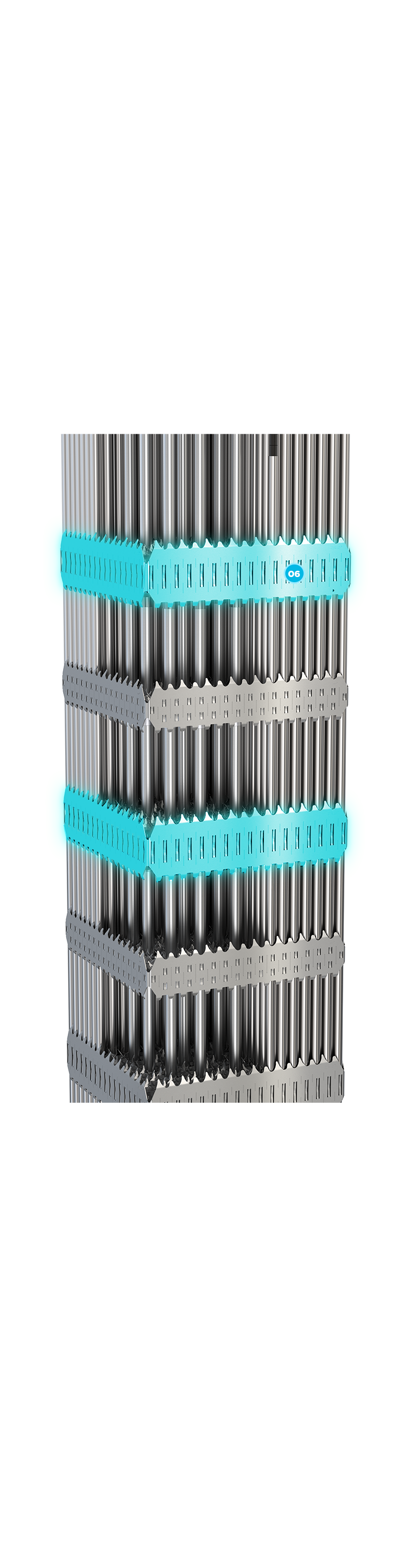
Fabricated from Low Tin ZIRLO material, which provides low neutron absorption and high corrosion resistance at high burnup. The mid grids have springs and dimples integral to the straps, to provide fuel rod support.
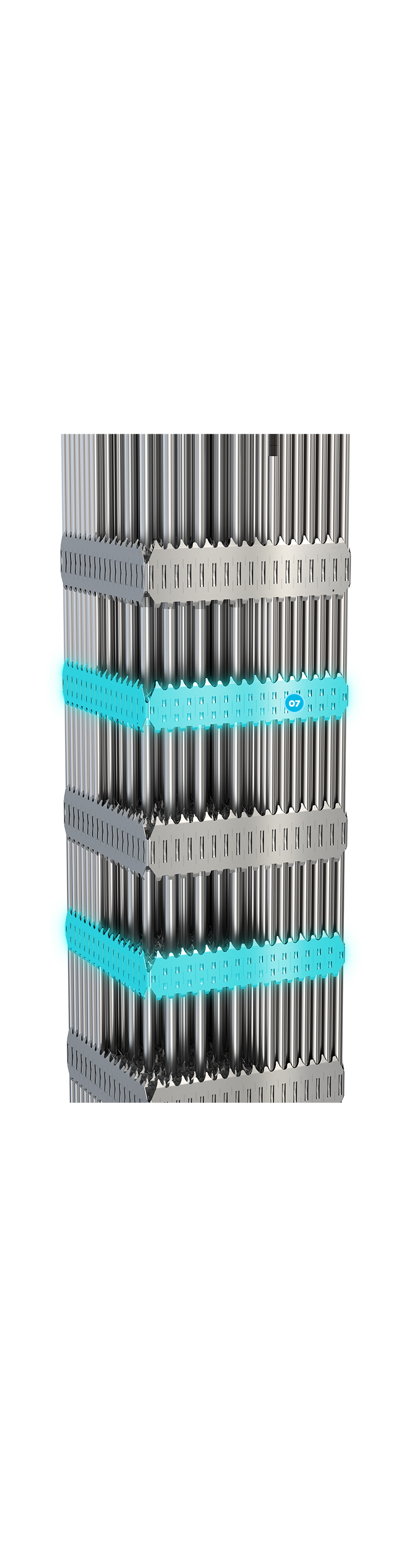
Fabricated from Low Tin ZIRLO material, which provides low neutron absorption and high corrosion resistance at high burnup. The IFM grid provides additional coolant mixing and improves thermal margins.
A pellet stack partially coated with thin ceramic layer of ZrB2 containing boron isotope 10 (B10) as the burnable absorber material. This is unique to Westinghouse and has a long history of proven fuel cycle cost benefits.
Regular UO2 that is blended with Gadolinia (Gd2O3) as the burnable absorber material. This absorber is the most common in the nuclear industry for PWR, BWR and VVER types of reactors.
A hard, wear-resistant surface layer of ZrO2 that provides additional resistance to debris and grid-to-rod-fretting (GTRF) damage, especially at beginning of life conditions, when GTRF can be limiting.
A reinforced dashpot, either a tube-in-tube or external dashpot tube assembly design, to mitigate incomplete control rod insertion and stiffen the fuel structure for high burnup operation.
Composed of straps, which are brazed together to form the grid structure. The bottom grid has integral grid strap springs with a high force to maintain contact with the fuel rod through end of life.
Traps debris within the robust protective grid (RPG) so fretting will occur on the solid end plug and not the uranium bearing portion of the fuel rod.
Functions as the bottom structural element of the fuel assembly. The bottom nozzle side skirt is replaced by a filter to block debris from getting between assemblies in the PRIME bottom nozzle.
Top
Middle
Bottom
Select an area of the assembly to explore
01 + Alloy 718 Leaf Spring ]
02 + WIN Top Nozzle ]
03 + Alloy 718 Top Grid ]
04 + ADOPT Fuel Pellets ]
05 + AXIOM® Fuel Rod Cladding ]
06 + PRIME™ Low Tin ZIRLO™ - Structural Mid Grid ]
07 + PRIME™ Low Tin ZIRLO™ - Intermediate Flow Mixing Grid ]
08 + Integral Fuel Burnable Absorber ]
09 + Gadolinia Burnable Absorber ]
10 + Debris Resistant Oxide Coating ]
11 + Reinforced Tube-In-Tube Dashpot ]
12 + Alloy 718 Bottom Grid ]
13 + Robust Debris Protection Grid ]
14 + PRIME™ Debris Filter Bottom Nozzle ]