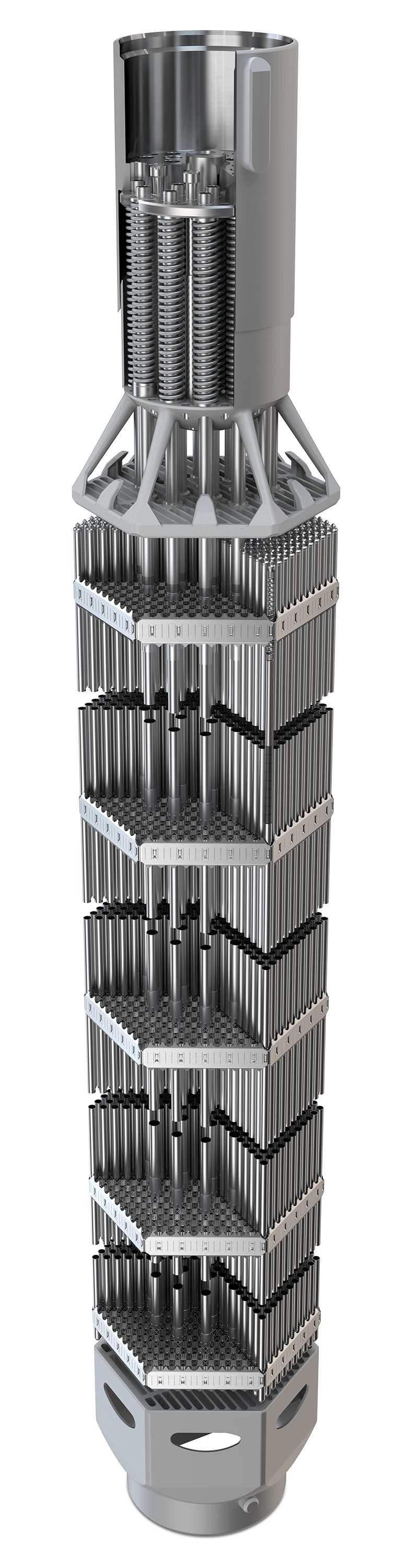
This design has rapidly become the Westinghouse standard fuel product for the VVER-1000 units. Mechanical features and stronger materials were introduced to improve robustness. The RWFA product has demonstrated excellent performance and reliability. It is designed for the conditions following planned power uprates as well as load follow operation.
Top of Assembly
Click on one of the features below to learn more about their benefits.
Middle of Assembly
Click on one of the features below to learn more about their benefits.
Bottom of Assembly
Click on one of the features below to learn more about their benefits.
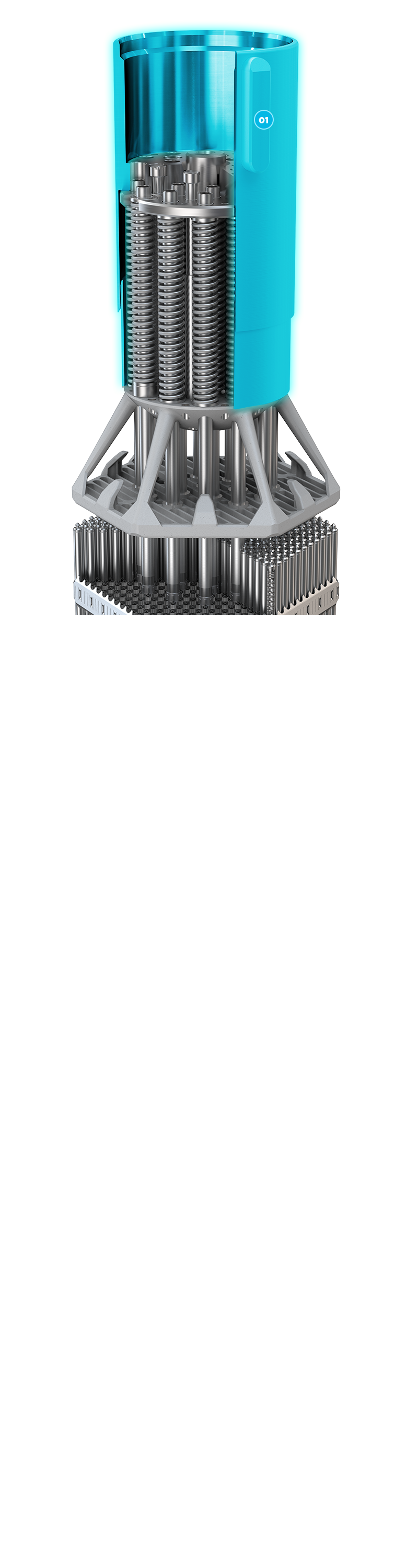
Made from stainless steel this is the interfacing surface for handling tools for alignment in the reactor. The barrel assembly is capable of deflecting to compensate for changes in the length of the fuel assembly.
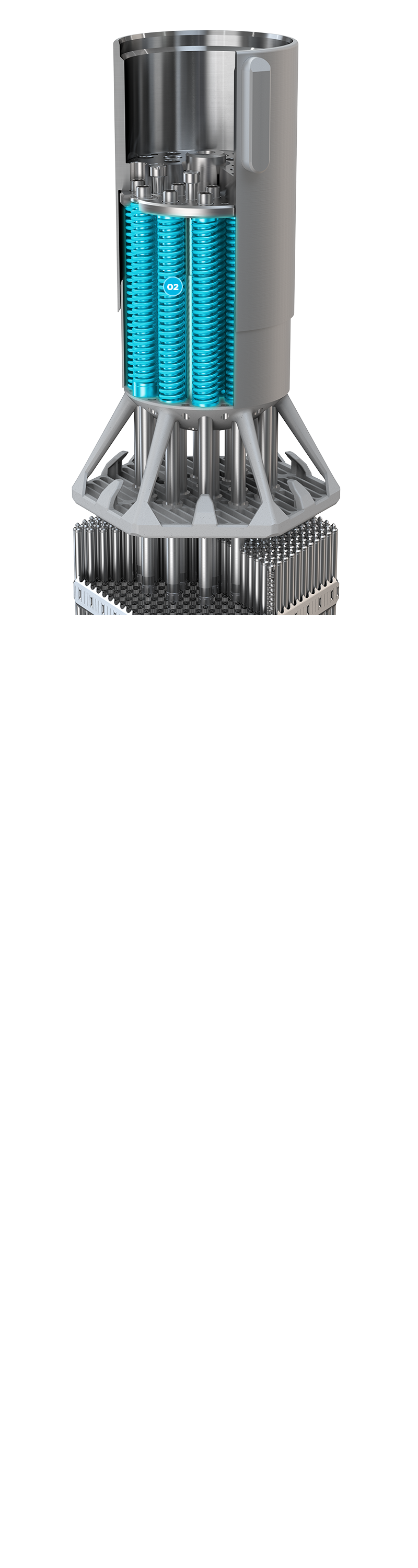
The 19 holddown springs of Alloy 718 provide the fuel assembly holddown force and the force to hold up the reactor internals. Provides the damping force in the event of an RCCA trip, also known as SCRAM.
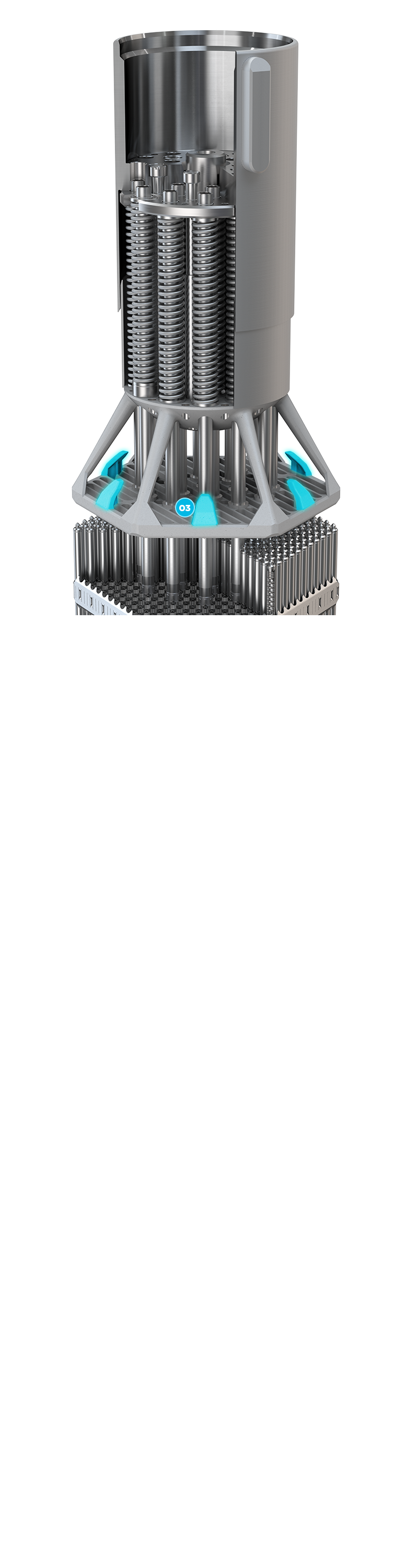
Deflectors are incorporated to eliminate nozzle hangup during core loading.
Composed of straps, which are laser welded together to form the grid structure and maintain contact force through end of life. The top grid has integral grid strap springs with a low force to mitigate fuel rod bow.
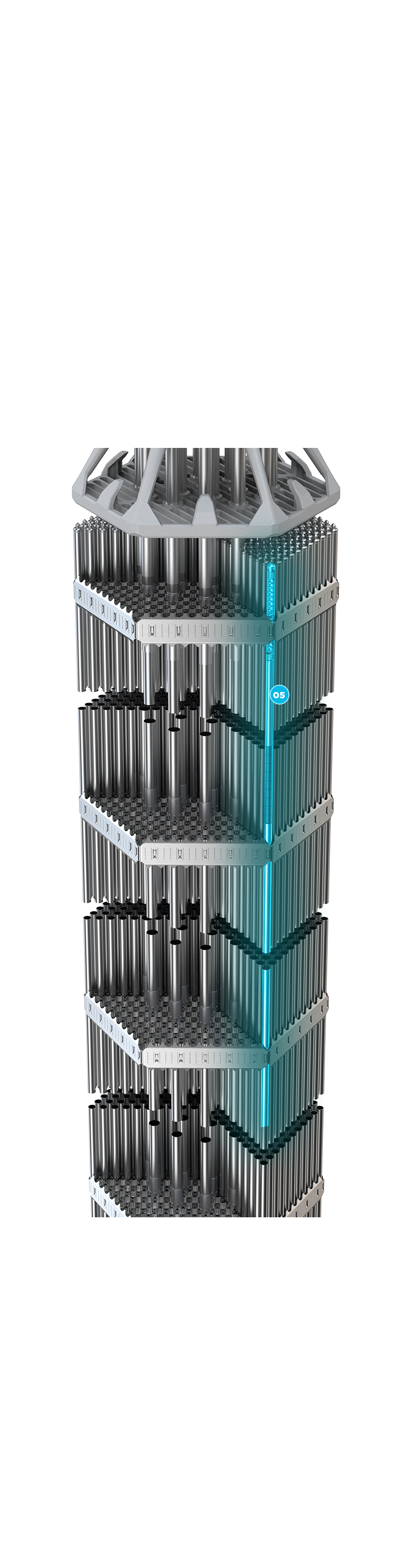
Made from Optimized ZIRLO™ which provides additional margin against corrosion. The fuel rod contains UO2 pellets stabilized by a plenum spring to mitigate pellet stack movement.
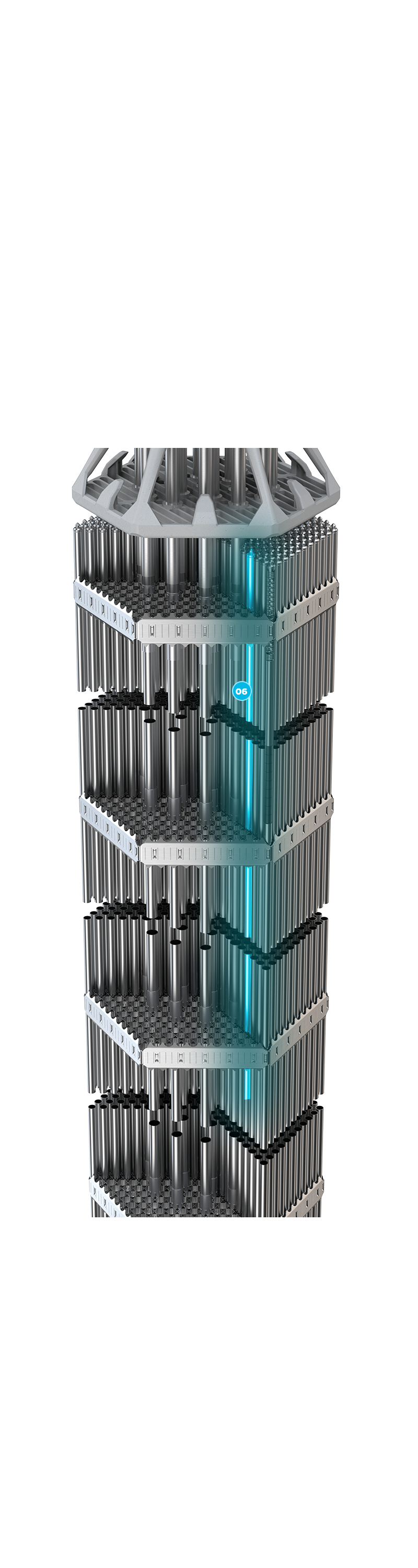
Regular UO2 that is blended with Gadolinia (Gd2O3) as the burnable absorber material. This absorber is the most common in the nuclear industry for PWR, BWR and VVER types of reactors.
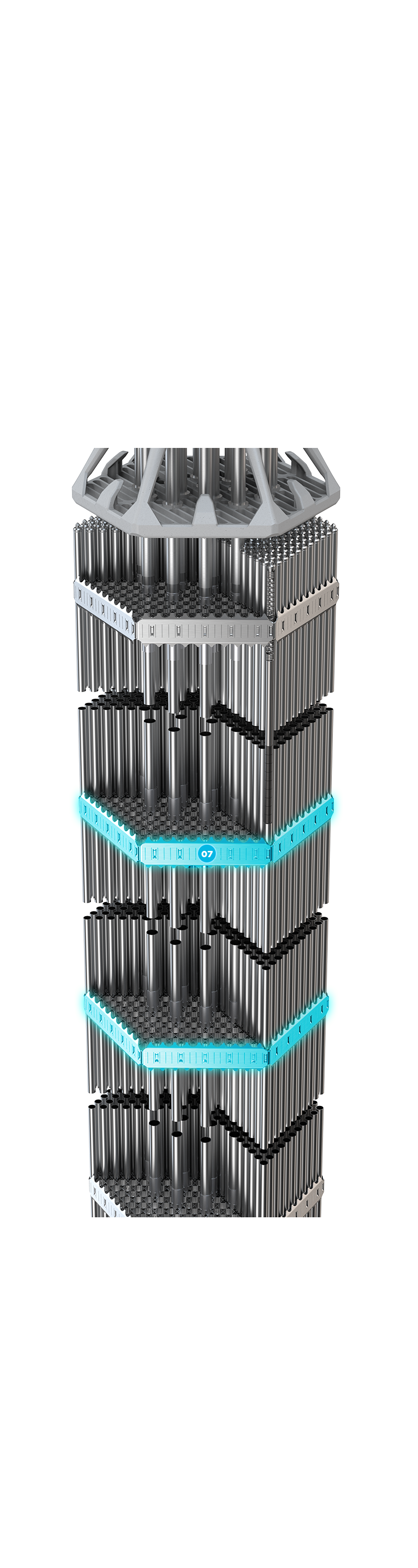
Fabricated from Alloy 718 or Zr1%Nb material. The mid grids have springs and dimples integral to the straps, to provide fuel rod support.
The 18 guide thimble tubes, of ZIRLO™ material, in the RWFA design do not have a dashpot, which is different than in the standard Westinghouse PWR designs.
The bottom grid has integral grid strap springs with a high force to maintain contact with the fuel rod through end of life. It directs the fuel growth rod in one direction from the bottom grid up toward the top of the fuel assembly.
The stainless steel bottom nozzle serves as the bottom structural element of the fuel assembly and directs the coolant flow distribution to the assembly.
Top
Middle
Bottom
Select an area of the assembly to explore
01 + Barrel Assembly ]
02 + Spring Package ]
03 + Deflectors ]
04 + Alloy 718 Top Grid ]
05 + Fuel Rod ]
06 + Gd Burnable Absorber ]
07 + Structural Mid Grid ]
08 + Guide Thimble Tube ]
09 + Bottom Grid ]
10 + Bottom Nozzle ]